‘Nature’ publica un traballo pioneiro sobre fisión nuclear no que participa o IGFAE



29.06.2021
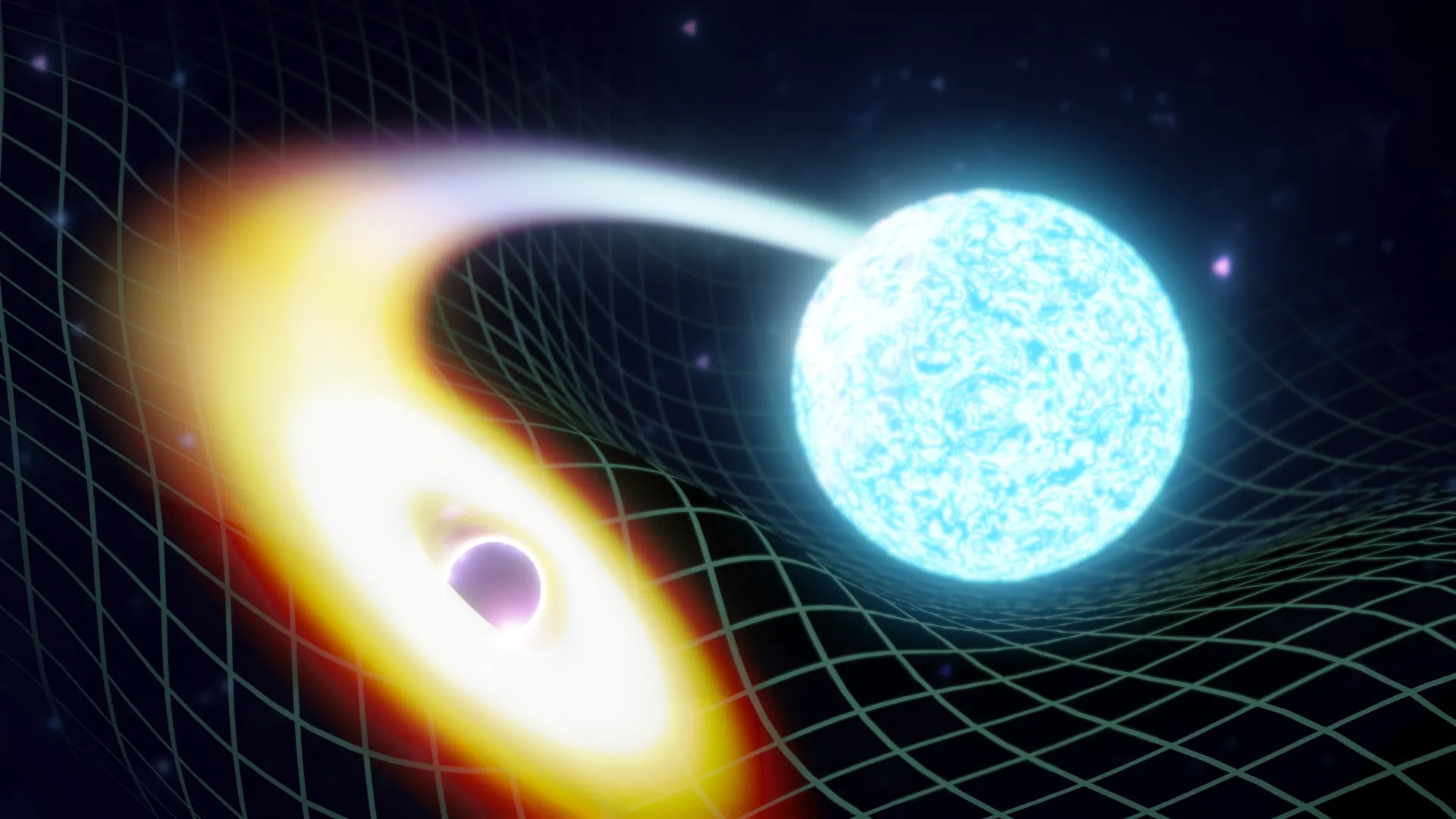
Por primeira vez, a comunidade científica confirma a detección dunha colisión entre un buraco negro e unha estrela de neutróns. De feito, non se detectou un, senón dous eventos deste tipo que se produciron con apenas 10 días de diferenza en xaneiro de 2020. Estes eventos extremos “engurraron” o espazo, producindo ondas gravitacionais que tardaron, polo menos, 900 millóns de anos luz ata chegar á Terra. En cada caso, a estrela de neutróns foi probablemente engulida polo seu compañeiro o buraco negro.
As ondas gravitacionais son perturbacións na curvatura do espazo-tempo creadas por obxectos masivos en movemento. Durante os cinco anos transcorridos desde que se mediron por primeira vez ‒achado que conduciu ao Premio Nobel de Física de 2017‒ identificáronse máis de 50 sinais de ondas gravitacionais procedentes da fusión de pares de buracos negros e de pares de estrelas de neutróns. Tanto os buracos negros como as estrelas de neutróns son os cadáveres de estrelas masivas, sendo os buracos negros aínda máis masivos que as estrelas de neutróns.
Agora, nun novo estudo, a comunidade científica anuncia a detección de ondas gravitacionais procedentes de dous raros eventos, cada un dos cales implica a colisión dun buraco negro e unha estrela de neutróns. As ondas gravitacionais foron detectadas polo Observatorio de Ondas Gravitacionais do Interferómetro Láser (LIGO) da National Science Foundation (NSF) en Estados Unidos e polo detector Virgo en Italia. O detector KAGRA, en Xapón, uniuse á rede LIGO-Virgo en 2020, pero non estaba en liña durante estas deteccións.
A primeira fusión, detectada o 5 de xaneiro de 2020, involucrou a un buraco negro dunhas 9 veces a masa do noso sol, ou 9 masas solares, e a unha estrela de neutróns de 1,9 masas solares. A segunda fusión detectouse o 15 de xaneiro e nela participaron un buraco negro de 6 masas solares e unha estrela de neutróns de 1,5 masas solares. Publícanse os resultados hoxe, 29 de xuño, en The Astrophysical Journal Letters.

Thomas Dent, investigador do IGFAE coordinador do programa de ondas gravitacionais, e Juan Calderón Bustillo, investigador “la Caixa Junior Leader” do mesmo programa que participaron neste achado. Crédito: Elena Mora (IGFAE).
Os astrónomos levan décadas buscando estrelas de neutróns que orbiten ao redor de buracos negros na Vía Láctea, a nosa galaxia, pero non atoparon ningunha ata o de agora. “Con este novo descubrimento de fusións de estrelas de neutróns e buracos negros fóra da nosa galaxia, atopamos o tipo de sistema binario que faltaba. Por fin podemos empezar a entender cantos destes sistemas existen, con que frecuencia fusiónanse e por que non vimos aínda exemplos na Vía Láctea”, afirma Astrid Lamberts, investigadora do CNRS no Observatorio da Costa Azul, en Niza (Francia).
O primeiro dos dous eventos, GW200105, foi observado polos detectores LIGOLivingston e Virgo. Produciu un forte sinal no detector LIGO pero tivo unha pequena relación sinal-ruído no detector Virgo. O outro detector LIGO, situado en Hanford (Washington), estivo temporalmente fóra de servizo. Dada a natureza das ondas gravitacionais, o equipo deduciu que o sinal foi causada por un buraco negro que chocou cun obxecto compacto de 1,9 masas solares, identificado posteriormente como unha estrela de neutróns. Esta fusión tivo lugar a 900 millóns de anos luz de distancia.
Debido a que o sinal foi forte nun só detector, a localización da fusión no ceo segue sendo incerta, situándose nalgún lugar dentro dunha área que é 34.000 veces o tamaño dunha Luna chea.
“Coa nosa sensibilidade actual non podemos identificar realmente os detalles sutís do sinal que nos permiten saber se estamos a presenciar buracos negros ou estrelas de neutróns”, afirma Juan Calderón Bustillo, investigador “la Caixa Junior Leader” no IGFAE. “Isto foi posible no caso de GW170817 porque tamén vimos a contrapartida electromagnética (luz). Con todo, teniendo en cuenta as masas que esperamos que teñan os buracos negros e as estrelas de neutróns, concluímos que os obxectos máis pequenos implicados nestas colisións son probablemente estrelas de neutróns”.
O segundo evento, GW200115, foi detectado tanto polos detectores LIGO como polo detector Virgo. GW200115 procede da fusión dun buraco negro cunha estrela de neutróns de 1,5 masas solares que tivo lugar a uns mil millóns de anos luz da Terra. “Como os tres instrumentos observaron este evento, puidemos excluír con moita máis precisión unha orixe de ruído terrestre: o método de procura PyCBC, desenvolto no IGFAE, descarta unha taxa de falsas alarmas superior a 1 por cada 50.000 anos”, explica Thomas Dent, líder do programa de ondas gravitacionais no IGFAE. “Aínda que a rede de tres detectores tamén axuda a acoutar a parte do ceo na que puido producirse o evento, esta zona seguía sendo case 3.000 veces máis grande que a Lúa chea”.
A alerta de ambos os eventos saltou pouco despois de que se detectasen os eventos en ondas gravitacionais e posteriormente buscaron no ceo os escintileos de luz asociados, pero non se atopou ningún. Isto non é sorprendente debido á gran distancia á que se atopan estas fusións, o que significa que calquera luz procedente delas, independentemente da lonxitude de onda, sería moi tenue e difícil de detectar mesmo cos telescopios máis potentes. Ademais, é probable que as fusións non emitisen moita luz en ningún caso porque os seus buracos negros eran o suficientemente grandes como para tragarse as estrelas de neutróns enteiras.
“Non se trata de eventos nos que os buracos negros cómanse as estrelas de neutróns, como o monstro das galletas, e “lanzar” anacos. Ese “lanzamento” é o que produciría a luz, e non cremos que iso ocorrese nestes casos”, afirma Patrick Brady, profesor da Universidade de Wisconsin-Milwaukee e voceiro da Colaboración Científica LIGO.
Anteriormente, a rede LIGO-Virgo atopou outras dúas candidatas a fusionar estrelas de neutróns con buracos negros. Un evento chamado GW190814, detectado o 14 de agosto de 2019, implicou unha colisión dun buraco negro de 23 masas solares cun obxecto de aproximadamente 2,6 masas solares, que podería ser a estrela de neutróns máis pesada coñecida ou o buraco negro máis lixeiro coñecido. Outro evento candidato, chamado GW190426, e detectado o 26 de abril de 2019, pensouse que posiblemente era unha fusión de estrela de neutróns e buraco negro, pero tamén podería ser simplemente o resultado do ruído do detector.
Tras observar con seguridade dous exemplos de ondas gravitacionais procedentes de buracos negros que se fusionan con estrelas de neutróns, estímase agora que, nun radio de mil millóns de anos luz da Terra, prodúcese aproximadamente unha fusión deste tipo ao mes.
“Os grupos de detectores de LIGO, Virgo e KAGRA están a mellorar os seus detectores para preparar o próximo ciclo de observación, que está previsto que comece no verán de 2022”, afirma Brady. “Coa sensibilidade mellorada, esperamos detectar as ondas de fusión ata unha vez ao día e medir mellor as propiedades dos buracos negros e a materia superdensa que compón as estrelas de neutróns”.
Información adicional sobre os observatorios de ondas gravitacionais:
Seis grupos españois contribúen ao estudo e análise das ondas gravitacionales detectadas por LIGO-Virgo, en áreas que van desde o modelado teórico das fontes astrofísicas e a análise dos datos ata a mellora da sensibilidade dos detectores para os períodos de observación actuais e futuros. Dous grupos, na Universitat de lles Illes Balears (UIB) e o Instituto Galego de Física de Altas Enerxías (IGFAE) da Universidade de Santiago de Compostela (USC), forman parte da Colaboración Científica LIGO; mentres que a Universitat de València (UV), o Instituto de Ciencias del Cosmos de Universidad de Barcelona (ICCUB), o Institut de Física d’Altes Energies (IFAE) de
Barcelona e o Instituto de Física Teórica (IFT) da Universidad Autónoma de Madrid-CSIC son membros de Virgo.
LIGO está operado por Caltech e o MIT, que concibiron LIGO e dirixiron o proxecto do detector Advanced LIGO. O proxecto LIGO Avanzado contou co apoio financeiro da NSF, pero tamén co de Alemaña (Sociedade Max Planck), o Reino Unido (Consello de Instalacións Científicas e Tecnolóxicas) e Australia (Consello Australiano de Investigación- OzGrav), que realizaron importantes compromisos e contribucións ao proxecto. Aproximadamente 1.400 científicos de todo o mundo participan no esforzo por analizar os datos e desenvolver deseños de detectores a través da Colaboración Científica LIGO, que inclúe a Colaboración GEO. A lista de socios adicionais está dispoñible en https://my.ligo.org/census.php
A Colaboración Virgo componse actualmente duns 650 membros de 119 institucións de 14 países diferentes, entre eles Alemaña, Bélxica, España, Francia, Hungría, Italia, Países Baixos e Polonia. O Observatorio Gravitacional Europeo (EGO) alberga o detector Virgo preto de Pisa (Italia) e está financiado polo Centre National da Recherche Scientifique ( CNRS) de Francia, o Istituto Nazionale dei Fisica Nucleare (INFN) de Italia e Nikhef dos Países Baixos. A lista dos grupos da Colaboración Virgo pode consultarse en http://public.virgo-gw.eu/the-virgo-collaboration. Pódese obter máis información no sitio web de Virgo en http://www.virgo-gw.eu .
O detector KAGRA está situado en Kamioka, Gifu, Xapón. O instituto anfitrión é o Instituto de Investigación de Raios Cósmicos (ICRR) da Universidade de Tokio, e o proxecto está coorganizado polo Observatorio Astronómico Nacional de Xapón (NAOJ) e a Organización de Investigación de Aceleradores de Alta Enerxía (KEK). KAGRA finalizou a súa construción en 2019, e posteriormente uniuse á rede internacional de ondas gravitacionais de LIGO e Virgo. A toma de datos propiamente dita iniciouse en febreiro de 2020 durante a etapa final do percorrido denominada “Ou3 b”. A colaboración KAGRA está composta por máis de 470 membros de 11 países/rexións. A lista de investigadores está dispoñible en http://gwwiki.icrr.utokyo.ac.jp/JGWwiki/KAGRA/KSC/Researchers. A información de
KAGRA atópase no sitio web https://gwcenter.icrr.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/
Referencias: R. Abbott et al 2021 ApJL 915 L5. “Observation of gravitational waves from two neutron star-black hole coalescences”. DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ac082e
Imaxe: Ilustración artística da fusión dun buraco negro e unha estrela de neutróns. Créditos: LIGO-India/ Soheb Mandhai.